آموزش حسابداری به زبان انگلیسی
آخرین ویرایش: مرداد 22, 1403



یادگیری حسابداری مرحلهای حیاتی برای ساختن یک حرفه موفق در دنیای تجارت است. آموزش حسابداری به زبان انگلیسی، نه تنها دانش و مهارتهای مورد نیاز برای انجام وظایف مختلف حسابداری به افراد را ارائه میدهد، بلکه فرصتهایی را فراهم میکند تا این دانش را با دیگران به اشتراک گذاشته و تأثیر مثبتی بر زندگی آنها داشته باشد.
پیشنهاد می شود مقاله اصطلاحات حسابداری به انگلیسی را نیز مطالعه نمایید.
حسابداری، بدون در نظر گرفتن اینکه “شما به دنبال فرصتهای شغلی جدید هستید”، یا “تمایل به انتقال دانش خود به نسل جدید هستید”، تجربهای رضایتبخش است. روشهای مختلفی برای تدریس حسابداری وجود دارد، که هر کدام از آنها دارای مزایا و معایب مختص خود هستند.
حسابداری ستون فقرات دنیای کسبوکار است؛ و بهعنوان یک وسیله مهم برای ارائه اطلاعات کمیِ شرکتها و واحدهای اقتصادی به منظور تصمیمگیریهای آگاهانه و انتخاب بهترین مسیر مورد استفاده، به ویژه در زمینه مالی، مورد استفاده قرار میگیرد. حسابداری تنها مفاهیم عددی نمیباشد؛ بلکه شامل پیگیری جریان نقدینگی روزمره به داخل و خارج از یک سازمان، حفظ تعادل مالی و پیشبینی مسائل آتی نیز میشود. یک حسابدار ماهر دانش عمیقی از پول، ریاضیات، آمار و اقتصاد دارد که همگی اساس رشد و موفقیت یک سازمان هستند. آموزش حسابداری با هدف آمادهسازی دانشجویان برای حرفههای حسابداری انجام میشود و بر اهمیت کاربرد عملی اصول حسابداری و ارتباط آن با سایر حوزهها تأکید مینماید.
ما در آموزشگاه حسابداری آپاداس، تلاش میکنیم بر اساس تجربه فعالیت 25 ساله استاد وحید قربانی در زمینه امور مالی، و تدریس بیش از 200 حسابدار فعال، بهترین دوره حضوری آموزش حسابداری در تبریز و کاربردیترین دوره حسابداری آنلاین را برگزار کنیم.
یکی از بخشهای اصلی حسابداری، حسابداری مالی است. این حوزه به تهیه و ارائه گزارشهای مالی اختصاصی دارد که به سهامداران، اعتباردهندگان و نهادهای نظارتی مانند: سازمانها و شرکتها، تصویر دقیقی از وضعیتمالی یک سازمان ارائه میدهد. موضوعات اصلی حسابداری مالی شامل: ترازنامه، صورت سودوزیان، گزارش جریان وجهنقد، و اصول حسابداری پذیرفته شده است. حسابداران در این زمینه نقش بسیار مهمی ایفا میکنند و تضمین مینمایند که گزارشهای مالی با استانداردهای تعیین شده هماهنگ باشند و تصویر شفافی از عملکرد مالی یک شرکت را ارائه دهند.
دیگر موضوع مهم در این زمینه، حسابداری مدیریتی است. برعکس حسابداری مالی که عمدتاً با گزارشدهی به خارج مشغول است، حسابداری مدیریتی بر تولید اطلاعات مالی داخلی برای کمک به تصمیمگیری و مدیریت تمرکز دارد. موضوعاتِ حسابداری مدیریتی شامل: بودجهریزی، تجزیه و تحلیل هزینهها، اندازهگیری عملکرد و برنامهریزی مالی است. حسابداران مدیریتی، اطلاعات ارزشمندی به تیمهای مدیریتی شرکتها ارائه میدهند و به آنها کمک میکنند تصمیمهای مطلوبی برای افزایش کارایی و سودآوری بگیرند.
حوزه دیگری که حائز اهمیت است، حسابداری مالیاتی است که به طراحی سیستمهای مالیاتی و پیامدهای مالیاتی میپردازد. حسابداران مالیاتی در زمینههای مرتبط با برنامهریزی مالیاتی، اطلاعات مالیاتی و استراتژیهای کاهش مالیات فعالیت میکنند. آنها با قوانین و مقررات مالیاتی خود را بهروز نگه میدارند؛ و به افراد و سازمانها کمک میکنند تا تعهدات مالیاتی خود را انجام دهند و در عین حال وضعیت مالیاتی بهتری داشته باشند. موضوعات حسابداری مالیاتی شامل: قوانین مالیات، کسر ویژگیهای مالیاتی، اعتبارات و تهیه اظهارنامه مالیاتی میباشد. حسابداران مالیاتی نقش اساسی در کمک به افراد و کسبوکارها برای مدیریت موقعیتهای پیچیده مالیاتی ایفا میکنند.


مهارتهای پایه برای موفقیت در حسابداری بسیار حیاتی هستند؛ زیرا این حوزه شامل: مدیریت اطلاعات مالی، تجزیه و تحلیل دادهها و اطمینان از دقت اسناد مالی میباشد. این مهارتهای ضروری به عنوان پایهای برای ایجاد تخصص و مراتب عالی در دنیای پیچیده حسابداری ایفا میکنند که شامل موارد زیر است:
اعداد: حسابداری بر اساس اعداد است. حسابداران با دادههای مالی کار میکنند، محاسبات را انجام میدهند و دادههای عددی را تجزیه و تحلیل میکنند. دانش ریاضیات یک مهارت کلیدی برای اطمینان از دقت دادههای مالی است. به منظور محاسبه هزینهها، درآمد، مالیات یا تهیه اظهارنامههای مالی، حسابداران باید بدانند چگونه با اعداد کار کنند تا تصمیمات مالی بگیرند. البته تنها داشتن دانش چهار عمل اصلی ریاضی برای انجام کار حسابداری کفایت میکند.
توجه به جزئیات: توجه به جزئیات در حسابداری بسیار مهم است. اشتباهات کوچک میتوانند پیامدهای بزرگی داشته باشند، بنابراین توجه به جزئیات مهم است. حسابداران مسئول ثبت دقیق تمام تراکنشهای مالی هستند و باید اطمینان حاصل کنند که تمام ورودیها دقیق هستند. توجه دقیق به جزئیات برای حفظ صداقت اطلاعات مالی ضروری میباشد.
مهارتهای سازماندهی: حسابداران حجم زیادی از داده، اسناد و مدارک مالی را مدیریت میکنند. برنامهریزی موثر، کلیدی برای مدیریت این اطلاعات بهصورت کاربردی است. بنابریان ضروری است که بتوانند ردیابی اظهارنامههای مالی، فاکتورها، صورتحسابها و سایر اسناد را انجام دهند. یک سیستم منظم اطمینان میدهد که اطلاعات خواسته شده در زمان مورد نیاز برای گزارشدهی مالی، حسابرسی یا تجزیه و تحلیل، آماده باشند.
تفکر تحلیلی: حسابداران فقط ثبتکنندههای اطلاعات نیستند؛ آنها متخصصان مالی نیز هستند. آنها باید اظهارنامههای مالی را برای شناسایی روندها، اشتباهات و مشکلات احتمالی، تجزیه و تحلیل کنند. مهارتهای تحلیلی برای درک دادههای مالی پیچیده، بهمنظور استخراج نتایج معنیدار لازم است. این مهارتها به حسابداران اجازه میدهد تا برای مشتریان یا سازمانها، نتایج و پیشنهادات ارزشمندی ارائه دهند.
مهارتهای ارتباطی: حسابداران باید اطلاعات مالی را بهوضوح بهصورت نوشتاری و شفاهی ارتباط دهند. اغلب از آنها خواسته میشوند که اظهارنامهها یا گزارشهای مالی را برای مشتریان، همکاران یا افراد غیرمالی تفسیر کنند. ارتباط مؤثر اطمینان میدهد که دیگران اطلاعات مالی ارائه شده را درک کرده و براساس آن تصمیمات آگاهانه بگیرند.
رفتار اخلاقی: حفظ صداقت اطلاعات مالی در حسابداری بسیار مهم است. حسابداران مسئول و نماینده دقیقِ وضعیت مالی یک سازمان هستند. پایبندی به استانداردهای اخلاقی و رعایت مقررات و قوانین حائز اهمیت است تا اعتماد و اعتبار در این حوزه ایجاد شود.
مهارتهای کامپیوتری: در دوران دیجیتال، دانش نرمافزارهای حسابداری و استفاده از صفحات گسترده برای مدیریت و تجزیه و تحلیل اطلاعات، اساسی است. حسابداران از انواع ابزارهای نرمافزاری برای انجام وظایفی مانند: حسابداری، مدلسازی مالی و تجزیه و تحلیل دادهها استفاده میکنند. درک مناسب از این ابزارها به بهبود عملیات مالی کمک میکند و به افزایش بهرهوری منجر میشود.
توانایی حل مسائل: حسابداران اغلب با چالشها و خطاهای مالی روبرو میشوند که باید برطرف شوند. توانایی شناسایی مشکلات، تجزیه و تحلیل آنها، یافتن علل اصلی و ارائه راهحلهای مناسب، یک مهارت مهم است. مهارتهای حل مسائل برای اطمینان از دقت اسناد مالی و حفظ وضعیت مالی سازمان ضروری است.
هوش تجاری: برای یک حسابدار، درک محیط تجاری جهت گرفتن اطلاعات و اخذ مشاوره ضروری است. برنامهریزان مالی باید درک داشته باشند که چگونه تصمیمات مالی بر وضعیت کلی سازمان تأثیر دارند. این موارد شامل: درک عملکرد شرکت، شرایط تجاری و پویایی بازار است، که به حسابداران امکان میدهد تا بتوانند بهصورت استراتژیک مشاوره مالی را ارائه دهند.
مدیریت زمان: حسابداران اغلب وظایف متعدد را همزمان مدیریت میکنند. مهارتهای موثر مدیریت زمان برای اولویتبندی کار، رعایت زمانبندی و اطمینان از انجام بهموقع گزارشهای مالی، اظهارنامههای مالی و وظایف دیگر، بسیار ضروری هستند.
انطباقپذیری: صنعت حسابداری پویاست زیرا سیستمهای مالی، استانداردهای حسابداری و فنآوری در حال تحول هستند. حسابداران باید به مقررات جدید، نرمافزارهای حسابداری و فنآوریهای جدید آشنا بوده و تناسبپذیری داشته باشند تا بتوانند از پایداری و کارآیی در ایفای نقش خود برخوردار باشند.
این مهارتهای پایه به عنوان بخش سازنده برای ایجاد حرفه موفق در حسابداری عمل میکنند. با پیشرفت در حرفه حسابداری، میتوان مهارت و دانش خود را در زمینههایی مانند: حسابداری مالی، حسابرسی، تجزیه و تحلیل مالی توسعه داد. حسابداری یک حرفه متنوع است که دربرگیرنده شغل های مختلفی می باشد. مهارتهای اساسی یک پایه قوی برای حسابداران فراهم میکنند تا در حوزه انتخابی خود به برتری دست یابند و تصمیمات مالی خوبی را در محیط مالی پویا بگیرند.
Accounting education is a crucial step towards building a successful career in the world of business. Not only does it equip individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary for various accounting roles, but it also opens up opportunities to share this expertise with others, making a positive impact on their lives.
Accounting is a fulfilling endeavor, whether you’re exploring new career opportunities or seeking to pass on your knowledge to the next generation. There are diverse methods of teaching accounting, each with its own advantages and drawbacks.
Accounting, as a subject, forms the backbone of the business world. It serves as a means to provide quantitative data, predominantly financial, about economic entities, enabling informed decision-making and the selection of optimal courses of action. Accounting extends beyond mere numbers; it involves tracking daily cash flows in and out of an organization, maintaining financial equilibrium, and proactively averting potential issues. A competent accountant possesses a deep understanding of money, mathematics, statistics, and economics, all of which are fundamental to an organization’s growth and success. Accounting education is conducted with the aim of preparing students for careers in accounting and emphasizes the importance of the practical application of accounting principles and their relevance to other fields.
One of the major divisions of accounting is financial accounting. This area is devoted to the preparation and presentation of financial statements that provide external stakeholders such as shareholders, creditors, and regulators with an accurate view of the financial health of an organization. Basic accounting topics include the balance sheet, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Accountants play a very important role in ensuring that financial statements conform to established standards and provide a clear picture of a company’s financial performance.
Another important issue is management accounting. Unlike financial accounting, which is primarily concerned with external reporting, management accounting focuses on generating internal financial information to aid decision-making and management. Management accounting topics include budgeting, cost analysis, performance measurement, and financial planning. Account managers provide valuable information to corporate management teams and help them make informed decisions to increase efficiency and profitability.
Tax accounting is a special system that deals with taxes and their financial consequences. Tax accountants work in areas related to tax planning, compliance and tax mitigation strategies. They remain knowledgeable about tax laws and regulations and help individuals and organizations meet their tax obligations while improving their tax position. Tax accounting topics include tax laws, tax credits, credits and tax return preparation. Tax accountants play a key role in helping individuals and businesses navigate complex tax situations.
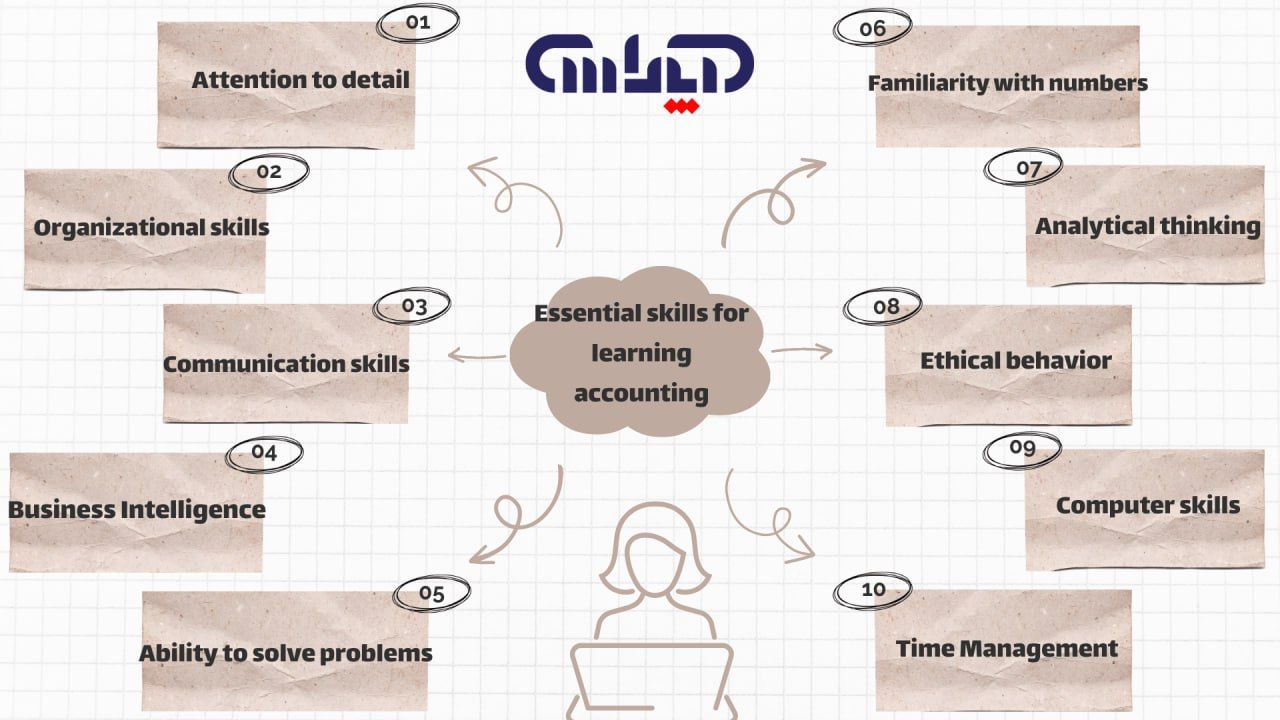

Basic skills are critical to success in accounting, a field that involves managing financial information, analyzing data, and ensuring the accuracy of financial records. These essential skills serve as the foundation for building expertise and excellence in the complex world of accounting which includes the following:
Numbers: Accounting is based on numbers. Accountants work with financial data, regularly perform calculations and analyze numerical data. Knowledge of mathematics is a key skill for ensuring the accuracy of financial data. Whether it’s calculating expenses, income, taxes, or preparing financial statements, accountants need to know how to work with numbers to make financial decisions.
Attention to detail: Attention is important in accounting. Small mistakes can have big consequences, so details are important. Accountants are responsible for accurately recording all financial transactions and ensuring that all entries are accurate. Meticulous attention to detail is essential to maintaining the integrity of financial information.
Organizational Skills: Accountants manage large amounts of data, documents, and financial records. Effective planning is key to effectively managing this information. It is important to be able to keep track of financial statements, invoices, bills and other documents. A proper system ensures that information is readily available when needed for financial reporting, auditing or analysis.
Analytical thinking: Accountants are not just record keepers. They are also financial experts. They must analyze financial statements to identify trends, errors and potential problems. Analytical skills are required to understand complex financial data and draw meaningful conclusions. These skills allow accountants to provide valuable insight and advice to clients or organizations.
Communication Skills: Accountants must communicate financial information clearly, both in writing and orally. They are often asked to interpret financial statements, tax returns or financial reports for clients, colleagues or non-financial professionals. Effective communication ensures that others understand the financial information presented and make informed decisions based on that information.
Ethical judgment: Maintaining the integrity of financial information is essential in accounting. Accountants have a responsibility to accurately represent the financial health of an organization. Adherence to ethical standards and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements are essential to building trust and credibility in this field.
Computer skills: In the digital age, knowledge of accounting software and the use of spreadsheets is essential for effective data management and analysis. Accountants use a variety of software tools to perform tasks such as accounting, financial modeling, and data analysis. A good understanding of these tools will help improve financial operations and increase productivity.
Ability to solve problems: Accountants often encounter financial challenges and errors that need to be resolved. The ability to identify problems, perform root cause analysis, and develop appropriate solutions is an important skill. Problem-solving skills are essential to ensuring the accuracy of financial records and maintaining an organization’s financial health.
Business Intelligence: Understanding the broader business environment is essential to gaining valuable information and advice as an accountant. Financial planners must understand how financial decisions affect the overall health of the organization. This includes understanding the company’s performance, business conditions and market dynamics, enabling accountants to provide strategic financial advice.
Time Management: Accountants often manage multiple tasks and deadlines at the same time. Effective time management skills are essential to prioritizing work, meeting deadlines, and ensuring timely completion of financial reports, tax returns, and other tasks.
Adaptability: The accounting industry is dynamic as financial systems, accounting standards and technology evolve. Accountants must adapt to new regulations, accounting software and technology to remain relevant and effective in their role.
These basic skills serve as building blocks for building a successful accounting career. As the accounting profession progresses, skills and knowledge can be developed in areas such as tax accounting, auditing, financial analysis or bookkeeping. Accounting is a diverse profession that offers a variety of careers, from public accounting firms to corporate finance and government agencies. Fundamental skills provide a solid foundation for accountants to excel in their chosen field and make sound financial decisions in a changing financial environment.
این مقاله را به اشتراک بگذارید:
هانیه هاشمزاده، متولد 1367با حسابداری درمحیط کار بهصورت تجربی آشنا شد. وی دانشآموخته رشته مدیریت دولتی در مقطع کارشناسی و رشته مدیریت فنآوری اطلاعات در مقطع کارشناسی ارشد است. از فعالیت های فعلی خانم هانیه هاشم زاده، علاوه بر ارائه خدمات و آموزش حسابداری، مدیریت تیم محتوای تخصصی سایت، پیج اینستاگرامی، تنظیم دوره ها و تهیه جزوات میباشد.
وبسایت آموزشگاه حسابداری آپاداس علاوه بر ارائه مقالات حسابداری، دوره های آموزش حسابداری و فایل اکسل حسابداری نیز ارائه میکند. اگر در تبریز هستید و به دنبال آموزشگاه حسابداری معتبر میگردید، شرایط شرکت در دوره و سایر اطلاعات مربوطه را در صفحه آموزش حسابداری در تبریز آپاداس میتوانید مشاهده فرمایید. همچنین دوره آموزش آنلاین حسابداری آپاداس به شما این امکان را میدهند که مهارتهای لازم برای مدیریت مالی شرکت خود را کسب کنید و با استفاده از فایلهای اکسل آماده، کارایی و دقت بیشتری در کار خود داشته باشید.









